Introduction
Zeaxanthin is a carotenoid, a type of pigment found in many fruits and vegetables. It is particularly abundant in yellow and orange fruits and vegetables, such as bell peppers, corn, and oranges. Zeaxanthin supplement significantly contributes to eye health and is often included in dietary zeaxanthin supplements marketed for this purpose. It is specifically found in the eye’s macula, the area responsible for central vision and color perception. Research suggests that zeaxanthin protects the macula from damage caused by exposure to blue light and other forms of oxidative stress. In this blog, we’ll deliver all the information regarding the best zeaxanthin supplement in the World that will boost your health status to a great extent.

Find The Best around the world
Australia
Canada
France
Germany
India
Italy
Japan
Netherlands
Singapore
Spain
Sweden
UAE
UK
USA
Tips for choosing the right zeaxanthin supplement for you
Zeaxanthin is found in various natural products, especially fruit and vegetables. However, purchasing 100% organic veggies and raw materials might be beyond everyone’s reach because those are not cost-effective for real. Besides people, these days are part of the rat race and don’t even get enough time to eat properly. Supplements and multivitamins are the best solutions where they get an adequate amount of zeaxanthin. Apart from vegetables and fruits, some types of seafood like salmon, scallops, lobster, shrimp, and crayfish also contain some amount of zeaxanthin
Some of the best dietary sources of zeaxanthin include:
Corn: One of the richest sources of zeaxanthin, with a single ear of yellow corn providing around 5 to 10 milligrams of the nutrient.
Bell peppers: Both yellow and red bell peppers contain zeaxanthin, with red peppers having a higher amount.
Kale and other leafy greens: Kale, spinach, and collard greens all contain zeaxanthin, but in smaller amounts than other sources.
Peaches: Fresh peaches contain moderate levels of zeaxanthin.
Eggs: Some eggs from chickens fed a diet enriched with marigold extract, which is rich in zeaxanthin, are also a good source of zeaxanthin.
Paprika: Paprika is a type of pepper ground into a powder. It’s another good source of zeaxanthin.
Persimmons: Both American and Asian persimmons contain zeaxanthin
When purchasing a zeaxanthin supplement, there are several things to consider to ensure that you get a high-quality product that meets your needs.
Dosage:
Look for a supplement that provides at least 10 milligrams of zeaxanthin per serving, as this is the amount that has been used in most studies on the nutrient’s effects on eye health.
Form:
Zeaxanthin is available in several forms, including capsules, tablets, and soft gels. Choose the form that you prefer and find it most convenient to take.
Purity:
Look for supplements certified by an independent third-party organization as pure and free of contaminants such as heavy metals or pesticides.
Brand reputation:
Research the supplement brand and look for any negative reviews or complaints. It’s always better to go with a reputable brand with a good track record.
Ingredients:
Check the supplement label for the list of ingredients and ensure the supplement contains only the ingredient you want and nothing else that may cause an allergic reaction.
Price:
Shop around and compare prices of different brands and forms of zeaxanthin supplements. Be aware that some brands of supplements may be more expensive but still not of higher quality.
Consult with a professional:
Before starting any supplement, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any health conditions or are taking any medications.
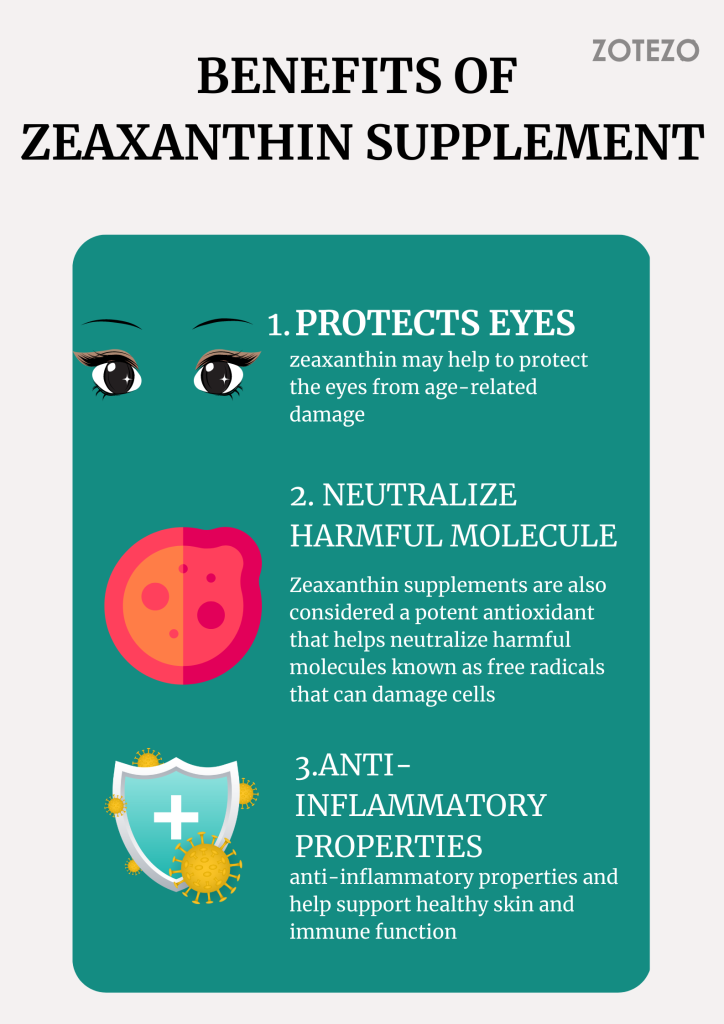
Benefits of using zeaxanthin supplement
Zeaxanthin plays two crucial roles:
- It builds a yellow-colored pigment shield to protect eye cells from the harmful effects of specific light sources, such as the sun.
- It protects the eyes from dangerous free radicals and unstable molecules that steal electrons from healthy cells, causing damage (known as oxidation).
Protects eyes:
One potential benefit is that zeaxanthin may help to protect the eyes from age-related damage. Studies have suggested that the compound may help prevent or slow down the progression of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
Neutralize harmful molecules:
Zeaxanthin supplements are also potent antioxidant that helps neutralize harmful molecules known as free radicals that can damage cells and contribute to developing chronic diseases like cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
Anti-inflammatory properties:
Zeaxanthin may have anti-inflammatory properties and help support healthy skin and immune function. However, it is essential to note that more research is needed to confirm these potential benefits and to determine the most effective dosage for supplement use.
However, while zeaxanthin supplements may be beneficial, it’s still important to eat a healthy diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, as these foods contain not only zeaxanthin but also many other beneficial nutrients are essential for good health.
Side-effects of using zeaxanthin supplement
Common side effects of zeaxanthin supplements may include:
Digestive problems:
Often, it has been noticed that zeaxanthin supplements cause problems like nausea, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. It’s also possible that high doses of zeaxanthin may cause stomach cramps. It’s important to note that everyone’s body is different and can react differently to supplements. Also, it’s not uncommon for people to experience stomach cramps with supplements, especially when starting them. This could be due to their bodies not being used to the supplement or the timing of when it is taken.
Allergic reactions:
Allergic reactions such as skin rash, hives, or itching to supplements can be caused by ingredients, such as fillers, binders, or excipients, that are added to the supplement to improve its stability or to make it easier to swallow. These ingredients may be derived from nuts, wheat, gluten, or other common allergens.
Additionally, the capsules themselves can be an issue if the person is allergic to the material they are made of. If you are taking other supplements or medications that affect blood clotting or on blood thinners, you should consult your doctor or health care professional before taking zeaxanthin supplements.
Quantity of zeaxanthin:
The supplement industry is not well-regulated. Some products may not contain the amount of zeaxanthin stated on the label or other ingredients that are not listed. This can result in an ineffective product or one with unexpected side effects. It is important to always buy from reputable and trusted sources.
Overdose:
Another potential problem with zeaxanthin supplements is that, as with all supplements, they can overdose on them. High doses of zeaxanthin can cause toxicity and increase the risk of side effects. As a result, it’s crucial to speak to a healthcare professional and follow the recommended dosage when taking zeaxanthin supplements.
Recommended Dosage of zeaxanthin supplement
The effective dosage of zeaxanthin supplements can vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s age, sex, overall health, and the condition being treated.
Based on research studies, most dosage range from 2 to 10 mg of zeaxanthin per day, but some studies have used higher dosages. It’s important to note that supplement dosages can vary depending on the manufacturer and product. It’s always best to speak to a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen. They can help you determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs and monitor your progress to ensure that the supplement is safe and effective.
A balanced diet with various fruits and vegetables should provide you with enough zeaxanthin. Therefore, a supplement may not be necessary. Always be vigilant when taking supplements, follow the recommended dosage, and consult a healthcare professional.
Do you represent a health, nutrition, beauty, or fitness brand?
Share your brand story, and its philosophy with our millions of readers looking for the highest quality products for their well-being. We understand that your products cater to the unique needs of an individual; here’s your opportunity to share the purpose and unique value proposition of your products that you’ve so caringly created for their well-being.
Share your brand story
Frequently asked questions on zeaxanthin supplement
1. How should I take zeaxanthin supplements?
2. Are there any precautions or warnings related to zeaxanthin supplements?
3. Can I get enough zeaxanthin from my diet?
4. How much zeaxanthin should I take?
5. XZCan I get zeaxanthin from food?
Are you a health, nutrition, beauty or fitness expert?
Inviting all health, fitness, beauty, and wellness experts from around the world to join Zotezo, the ultimate trust commerce platform, and empower millions to make the right decisions for their wellbeing. Share your knowledge, review the highest quality products, and provide valuable insights to our engaged audience. Together, let's create a healthier, happier world!
Join our expert advisory board
Conclusion
Zeaxanthin is a carotenoid found in various fruits and vegetables and is also available in supplement form. Some research has suggested that zeaxanthin may have potential health benefits, like protecting the eye and preventing cell damage. It also helps in blood thinning to whoever is required, but of course, the guidance of a medical expert is needed. Also, if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, we recommend you not take a zeaxanthin supplement. So before opting for a zeaxanthin supplement, read more about the pros and cons.